Fixed Cost
As cost which is unaffected by the fluctuation in the level of activity(within a time period is known to be a fixed cost)
Eg:
Rent paid for the factory premises would not be affected by the output levels of that factory. Hence it is a
fixed cost.
- Fixed cost cost cannot be avoided in the short run due to its fixed nature.
- Fixed costs are incurred according to the time elapsed, rather than the changes in the level of activity.
- Fixed cost per unit will decrease when output increases
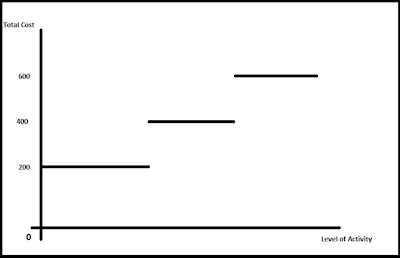
Stepped Fixed Cost(Step Cost)
When the cost is constant, within a certain level of activity and once you reach a critical level of activity, cost moves to the next step.
Eg:
Hiring cost of a machine which can produce 1000 units is 2000 Pounds. To produce the first 1000 units you need only 1 machine. If you are to produce 1001 units, you need to hire another machine. To produce the 2001st unit you need to hire the third machine. Here the cost would increse step by step.
Variable Cost
Cost that varies with the level of activity is called variable cost.
Eg:
Cost of raw materials
Cost of direct labour
This cost could be avoided in the short-run. Variable cost could be directly controlled by the management by changing the the output. It's not a periodic cost
Variable cost per unit will remain a constant(generally & most commonly)
Semi-Variable Cost
Cost containing both fixed & variable components are called semi-variable costs.
Variable Cost
Cost that varies with the level of activity is called variable cost.
Eg:
Cost of raw materials
Cost of direct labour
This cost could be avoided in the short-run. Variable cost could be directly controlled by the management by changing the the output. It's not a periodic cost
Variable cost per unit will remain a constant(generally & most commonly)
Semi-Variable Cost
Cost containing both fixed & variable components are called semi-variable costs.